On July 25, 2022, the team of Prof. Jianping Weng from University of Science and Technology of China published a feature review article entitled “Mouse Models of Atherosclerosis in Translational Research” in Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. Weng team was invited to review the current preclinical utility and translation potential of traditional [apolipoprotein E (APOE)- and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor (LDLR)-deficient mice] and emerging mouse models that includes partial carotid ligation and AAV8-Pcsk9-D377Y injection in atherosclerosis research and drug discovery. This article represents an important resource in atherosclerosis research. Authors also discuss factors to consider in utilizing mouse models in atherosclerosis research and offer their perspective on evaluating the various models.

Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, the major cause of premature human mortality, is a chronic and progressive metabolic and inflammatory disease in large- and medium-sized arteries. Therefore, seeking novel therapies for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a great medical need. In this regard, preclinical animal models, mouse models in particular, are widely used to gain mechanistic insights into the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Mouse models of atherosclerosis have been useful in validating the anti-atherosclerotic effects of many lipid-lowering drugs as well as anti-inflammation-based pharmacotherapies. In addition, mouse models have facilitated the discovery of anti-atherosclerotic drugs. Despite promising preclinical studies, many drug candidates have not translated to clinical usage due to the complexity of disease patho-mechanisms, including lipid metabolic traits, inflammatory, genetic, and hemodynamic factors. There are many factors that need to consider in utilizing mouse models in translational atherosclerosis research.
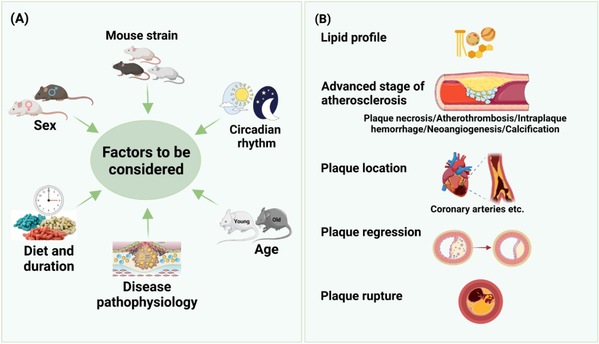
Figure: Factors to consider in utilizing mouse models in atherosclerosis research
Therefore, this article reviewed the current preclinical utility and translational potential of traditional and emerging models of atherosclerosis for understanding basic research questions, and exemplified their utilization in drug discovery and repurposing efforts. We also present the mode of atherosclerosis development, advantages, limitations and applications of different mouse models used in atherosclerosis research.
Professor Weng Jianping and Investigator Xu Suowen from the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China are the corresponding authors of the paper, and doctoral student Iqra Ilyas is the first author of the paper.
Original link: https://www.cell.com/trends/pharmacological-sciences/fulltext/S0165-6147(22)00136-5